In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations are continuously seeking tools that can streamline operations, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. Microsoft Power Platform stands out as a leading solution in this pursuit. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth Microsoft Power Platform overview, exploring its architecture, capabilities, and the certifications available for professionals. As businesses increasingly prioritize digital transformation, understanding the Power Platform becomes essential for maximizing efficiency and achieving strategic goals.
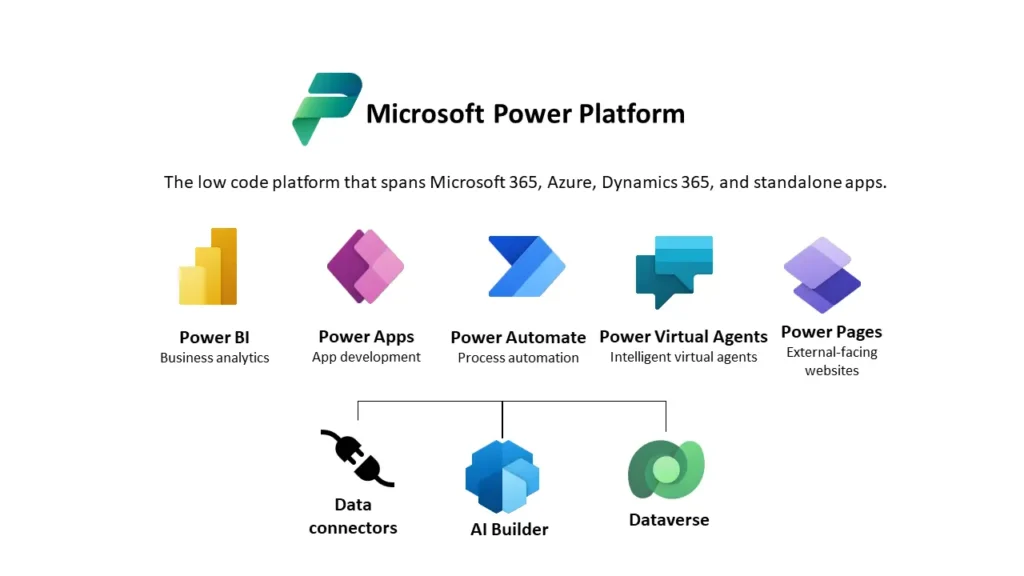
Microsoft Power Platform is a suite of applications, connectors, and data platforms that empowers users to create custom business solutions, automate workflows, and analyze data with ease. Comprising Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents, the platform offers a robust framework for addressing diverse business needs. This guide will delve into each component, elucidating their unique features and integration capabilities.
Moreover, we will explore the Microsoft Power Platform architecture, detailing how its components interact to deliver a cohesive and scalable environment for digital innovation. For those looking to validate their expertise, the guide will also highlight the various Microsoft Power Platform certification paths, providing insights on how to become a certified professional.
Whether you are a business leader aiming to drive digital transformation, an IT professional seeking to enhance your skills, or a developer eager to leverage low-code solutions, this guide will serve as a valuable resource. Join us as we unlock the full potential of Microsoft Power Platform, and discover how it can revolutionize the way you work and innovate.
What is Microsoft Power Platform?
Microsoft Power Platform is a suite of applications, connectors, and a data platform that provides a comprehensive environment for business automation, app development, and data analysis. It encompasses four core components: Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents. Each of these components serves a unique purpose, yet they work synergistically to enable organizations to streamline business processes, foster data-driven decision-making, and drive digital transformation.
Power BI is a business analytics tool that enables users to visualize data and share insights across their organization. It connects to a multitude of data sources, providing interactive reports and dashboards that help users make informed decisions. Power Apps allows users to build custom applications with minimal coding, enhancing the ability to solve business problems efficiently. Power Automate, previously known as Microsoft Flow, automates workflows between applications and services, reducing manual tasks and increasing productivity. Lastly, Power Virtual Agents enables the creation of intelligent chatbots that can engage with customers and employees alike, without requiring advanced coding skills.
The integration of Microsoft Power Platform with other Microsoft services, such as Azure, Dynamics 365, and Office 365, amplifies its capabilities. This seamless integration ensures that data flows effortlessly between applications, providing a unified and comprehensive approach to managing business processes. For instance, data from Dynamics 365 can be visualized in Power BI, automated with Power Automate, and acted upon using custom apps built with Power Apps.
Microsoft Power Platform plays a pivotal role in digital transformation by empowering organizations to adapt quickly to changing business needs. Its significance lies in its ability to democratize technology, allowing employees at all levels to contribute to process improvements and innovation. By enabling data-driven decision-making, it helps organizations become more agile, efficient, and competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment. As businesses increasingly rely on data to drive strategy, the importance of a robust and integrated platform like Microsoft Power Platform cannot be overstated.
Microsoft Power Platform Architecture
The Microsoft Power Platform is a cohesive suite of tools designed to enable comprehensive business solutions through a combination of various applications. At its core, the Power Platform consists of four primary components: Power Apps, Power Automate, Power BI, and Power Virtual Agents. Each of these components plays a distinct role, yet they are intricately interconnected to deliver a seamless experience for users.

Power Apps allows users to build custom applications with minimal coding. It empowers both professional developers and citizen developers to create tailored solutions that meet specific business needs. These applications can be deployed across various devices, providing flexibility and accessibility.
Power Automate, formerly known as Microsoft Flow, is a tool for automating workflows and business processes. It facilitates the creation of automated sequences that can handle repetitive tasks, integrate with numerous applications, and respond to triggers, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Power BI is a powerful analytics tool that enables users to visualize data and gain actionable insights. Through interactive dashboards and reports, Power BI transforms raw data into meaningful information that can drive informed decision-making.
Power Virtual Agents (aka. Copilot Studio) provides an intuitive interface for creating sophisticated chatbots. Without requiring any coding expertise, users can develop bots that interact with customers and employees, delivering automated responses and assisting with various tasks.
Power Pages is a robust, business-level, minimal-code SaaS solution that enables the development, hosting, and management of contemporary websites for external business use. Individuals with low-code skills can swiftly design, set up, and launch websites that function flawlessly across various web browsers and devices. Expert developers have the opportunity to enhance these functionalities to meet complex business needs.
Power Platform Data Connectors: Underlying the Power Platform is a robust framework of data connectors and integration capabilities. These connectors enable seamless connectivity with a wide range of Microsoft services, such as Dynamics 365 and Azure, as well as third-party applications. This interoperability ensures that data can flow effortlessly between different systems, enhancing the platform’s versatility and utility.
Microsoft Dataverse: Furthermore, the Common Data Service (CDS), now known as Microsoft Dataverse, acts as a unified data repository that standardizes data management across the Power Platform. Dataverse ensures data consistency and accessibility, providing a reliable foundation for building integrated solutions.
AI Builder is a feature integrated into Microsoft’s Power Apps and Power Automate that empowers teams to automate processes and predict outcomes using Microsoft’s AI technology. It provides a user-friendly, point-and-click experience for building AI models, which can be swiftly incorporated into both canvas and model-driven apps to enhance their intelligence. This introduction encapsulates the essence of AI Builder’s capabilities and its application within the Power Platform. It serves as a powerful tool for both automating processes and enhancing app intelligence. Whether you’re a novice or an expert, AI Builder is designed to make AI accessible and beneficial for everyone.
In summary, the architecture of Microsoft Power Platform is characterized by its modular yet interconnected components. The platform’s ability to integrate with various services and applications makes it a powerful tool for driving digital transformation and optimizing business processes.
Microsoft Power Platform Certification
Microsoft Power Platform certifications are designed to validate the expertise of professionals in leveraging the platform’s tools to drive business solutions. These certifications span various levels of proficiency, starting from fundamental to advanced, each tailored to meet specific career objectives and skill sets.
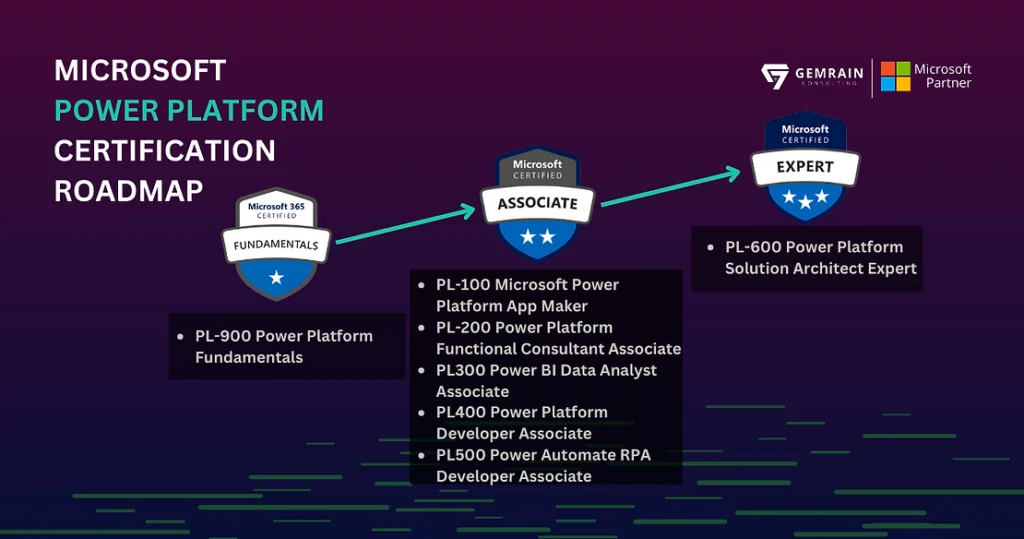
The PL-900: Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals certification is the entry-level credential. It is ideal for individuals new to the platform, covering the basic concepts and capabilities of Microsoft Power Platform services, including Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents. Achieving this certification demonstrates a foundational understanding of the platform, making it suitable for those seeking to start a career in this domain or enhance their existing skill set.
Moving to the next level, the PL-100: Microsoft Power Platform App Maker certification focuses on the creation of applications using Power Apps. It is designed for professionals who are responsible for building solutions to simplify, automate, and transform tasks and processes for their team. This certification requires a good grasp of data modeling, basic user experience design, and integration with Microsoft Power Platform services. Earning the PL-100 certification equips individuals with the skills to create robust, scalable apps that improve operational efficiency.
The PL-200: Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant certification targets those who work as functional consultants, analyzing business requirements and translating them into effective solutions using the platform. Candidates for this certification must have hands-on experience with the platform’s components and must be adept at configuring apps, creating dashboards, and managing data integrations. This certification validates the ability to implement and manage solutions that address business challenges, making it a valuable asset for career advancement as a consultant or project manager.
Obtaining Microsoft Power Platform certifications offers numerous benefits, including professional recognition, enhanced career prospects, and the potential for higher earnings. These certifications not only validate technical skills but also demonstrate a commitment to continuous learning and professional growth in an evolving technological landscape.
What is Microsoft Power Platform Dynamics 365?
Microsoft Power Platform is a suite of applications, connectors, and data platforms that provides a powerful set of tools to automate processes, build solutions, and analyze data. Dynamics 365, on the other hand, is a set of intelligent business applications that helps businesses manage customer relationships, financials, and operations. The integration between Microsoft Power Platform and Dynamics 365 creates a synergistic ecosystem, enhancing the capabilities of both platforms.
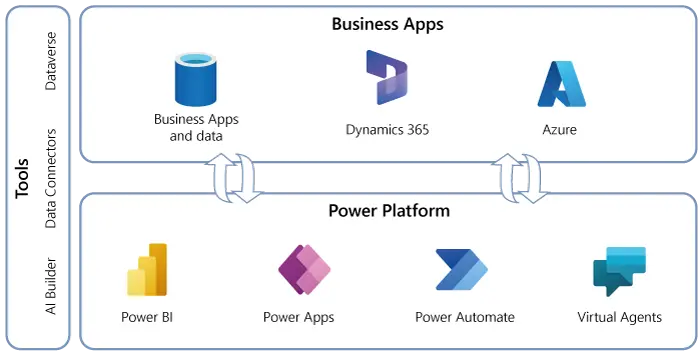
The seamless integration between Microsoft Power Platform and Dynamics 365 allows businesses to leverage the strengths of each platform. For instance, Power Apps can be used to build custom applications that interface with Dynamics 365 data, providing tailored solutions that meet specific business needs. Power Automate, another component of the Power Platform, can automate workflows across both Dynamics 365 and other applications, streamlining operations and reducing manual tasks.
One common use case of this integration is in customer relationship management (CRM). Dynamics 365 for Sales provides robust CRM capabilities, but businesses often require additional functionality. By using Power Apps, companies can create custom applications that enhance their CRM processes, such as a mobile app for field sales representatives that integrates directly with Dynamics 365. This enables real-time data entry and access, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Another example is in financial management. Dynamics 365 Finance allows businesses to manage financial operations, but integrating Power BI, a component of Microsoft Power Platform, can provide deeper insights through advanced analytics and reporting. Businesses can create interactive dashboards and reports that pull data from Dynamics 365, enabling more informed decision-making.
In summary, the integration between Microsoft Power Platform and Dynamics 365 extends the functionality of both platforms, allowing businesses to customize and enhance their operations. This powerful combination offers a flexible, scalable solution that can adapt to the unique needs of any organization, driving innovation and efficiency.
What is Power Platform Used For?
Microsoft Power Platform is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to empower businesses to automate processes, create custom applications, analyze data, and enhance customer interactions. Its versatility spans across various industries, making it a pivotal asset in the digital transformation journey of many organizations.
One primary use case of the Power Platform is automation. With Power Automate, businesses can streamline repetitive tasks, reducing manual labor and minimizing errors. For instance, a retail company can use Power Automate to automate inventory management, ensuring that stock levels are regularly updated and low inventory alerts are sent out promptly. This not only saves time but also enhances operational efficiency.
Custom application development is another significant application of the Power Platform. Power Apps allows businesses to create tailored applications without extensive coding knowledge. For example, a healthcare organization can develop a custom app to manage patient records, appointments, and billing processes. This ensures that the application meets specific needs while integrating seamlessly with existing systems.
Data analysis and visualization are crucial for informed decision-making, and Power BI is the tool within the Power Platform that excels in this area. Companies can harness Power BI to transform raw data into insightful reports and dashboards. A financial services firm, for instance, can analyze customer data to identify trends, predict market movements, and customize financial products accordingly.
Improving customer interactions is another critical use case for the Power Platform. By leveraging Power Virtual Agents, businesses can create intelligent chatbots that handle customer inquiries, provide support, and guide users through processes. In the travel industry, a company might deploy a chatbot to help customers book flights, manage reservations, and receive real-time updates, significantly enhancing the customer experience.
Overall, the Microsoft Power Platform is a multifaceted tool that adapts to the unique needs of various industries. From automating mundane tasks and developing custom apps to analyzing data and enhancing customer interactions, its applications are vast and impactful. By integrating the Power Platform, businesses can unlock new efficiencies, improve service delivery, and drive growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Power Platform vs Power Apps
Understanding the distinction between Power Apps and Power Platform is essential for leveraging the full potential of the Microsoft Power Platform. Power Apps is a suite within the Power Platform that allows users to create custom applications with little to no coding experience. These applications can be tailored to specific business needs, streamlining processes and enhancing productivity. On the other hand, Power Platform is a broader term that encompasses any application built using the capabilities of the entire Power Platform, including Power BI, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents.
Power Apps provides a user-friendly interface and a wide array of pre-built templates that enable rapid development and deployment. Users can create canvas apps, which offer a high degree of customizability and flexibility, or model-driven apps, which are more data-centric and leverage the Common Data Service (CDS) for seamless integration with other Microsoft services. For example, a sales team might use Power Apps to build a custom CRM solution that integrates with Dynamics 365, allowing them to manage leads and customer interactions more effectively.
Power Platform leverage the combined strengths of Power BI, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents to create comprehensive solutions that address various business challenges. For instance, a logistics company could develop an app that uses Power BI for real-time data visualization, Power Automate to streamline order processing workflows, and Power Virtual Agents to provide automated customer support. This integrated approach ensures that organizations can build robust, end-to-end solutions that enhance operational efficiency and decision-making.
One of the key advantages of using Microsoft Power Platform is the ease with which users can build and deploy custom applications. The platform’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface, extensive library of connectors, and strong community support make it accessible to both technical and non-technical users. This democratization of app development empowers employees across the organization to contribute to digital transformation initiatives, fostering innovation and driving business growth.
Microsoft Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate, formerly known as Microsoft Flow, serves as a cornerstone in the Microsoft Power Platform ecosystem. It facilitates the automation of workflows and business processes, enabling organizations to streamline operations and boost efficiency. By leveraging Power Automate, users can create automated workflows between various applications and services, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of human error.
One of the key features of Microsoft Power Automate is its use of triggers and actions. Triggers are events that initiate a workflow, such as receiving an email or updating a database. Actions are the steps that follow the trigger, such as sending a notification or creating a task in Microsoft Planner. This combination of triggers and actions allows users to construct complex workflows tailored to their specific needs.
Moreover, Power Automate offers a vast library of templates, providing pre-built workflows that can be easily customized. These templates cover a wide range of scenarios, from simple tasks like sending weekly reminders to more advanced processes such as automating approval workflows. By using templates, users can quickly implement automation without the need for extensive programming knowledge.
Integration with other Microsoft services is another significant advantage of Power Automate. It seamlessly connects with Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and Azure, as well as third-party applications like Salesforce, Google Drive, and Twitter. This extensive integration capability ensures that users can create cohesive workflows across different platforms, enhancing overall productivity.
Common automation tasks facilitated by Power Automate include data synchronization, automated notifications, and approval processes. For instance, a sales team can use Power Automate to automatically update a CRM system when a new lead is generated from a web form. Similarly, HR departments can streamline their onboarding processes by automating the distribution of welcome emails and task assignments to new employees.
In essence, Microsoft Power Automate empowers organizations to optimize their operations by automating repetitive tasks and integrating diverse applications. Its intuitive interface, coupled with robust features and extensive integrations, makes it an invaluable tool for driving efficiency and enhancing business workflows.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Microsoft Power Platform stands as a pivotal tool in the realm of digital transformation, offering businesses the ability to streamline processes, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have explored the core components of the Microsoft Power Platform, including Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents. Each of these components plays a crucial role in empowering organizations to build custom applications, automate workflows, analyze data, and create intelligent chatbots, all with minimal coding required.
The value of the Microsoft Power Platform is further amplified by its seamless integration with other Microsoft services such as Azure, Dynamics 365, and Microsoft 365. This interoperability ensures that businesses can leverage a holistic ecosystem to achieve their digital transformation goals. By adopting the Microsoft Power Platform, organizations can enjoy significant improvements in efficiency, agility, and decision-making capabilities.
Moreover, for professionals looking to advance their careers, obtaining certifications in the Microsoft Power Platform can provide a competitive edge. Certifications not only validate your skills but also demonstrate your commitment to staying abreast of the latest technological advancements. As the demand for expertise in low-code and no-code solutions continues to grow, being certified in the Microsoft Power Platform can open up new opportunities and career pathways.
We encourage readers to delve deeper into the capabilities of the Microsoft Power Platform and explore how it can be tailored to meet their unique business needs. By harnessing the power of this versatile platform, businesses can unlock new potentials and drive meaningful digital transformation.
#MSFTAdvocate #AbhishekDhoriya #LearnWithAbhishekDhoriya #DynamixAcademy
FAQs about Microsoft Power Platform
What is Microsoft Power Platform?
Microsoft Power Platform is an integrated suite of applications, connectors, and a data platform that provides tools to create and deploy custom business applications, automate workflows, analyze data, and engage with customers. It includes Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents, enabling users to enhance productivity and business processes without extensive coding knowledge.
What is the purpose of Microsoft Power Platform?
The primary purpose of Microsoft Power Platform is to empower businesses and individuals to easily build custom solutions to address specific business needs. By leveraging its components, organizations can automate repetitive tasks, visualize data insights, and create interactive applications, thus driving efficiency and innovation across various departments.
What language is Microsoft Power Platform?
Microsoft Power Platform primarily uses a low-code development approach, allowing users to build applications and automate processes with minimal coding. While the platform supports custom code in programming languages such as JavaScript and C#, particularly in Power Apps and Power Automate, it is designed to be accessible to a wide range of users, including those without traditional programming skills.
What is the difference between Power Apps and Power Platform?
Power Apps is one of the components within the Microsoft Power Platform. While Power Platform is the overarching suite that includes Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents, Power Apps specifically focuses on enabling users to create custom applications for various business scenarios. Essentially, Power Apps is a part of the broader Power Platform ecosystem.
What does a Microsoft Power Platform developer do?
A Microsoft Power Platform developer is responsible for designing, developing, and implementing solutions using the various tools within the Power Platform. This includes creating custom applications with Power Apps, automating workflows with Power Automate, generating data insights with Power BI, and building chatbots with Power Virtual Agents. These developers play a crucial role in modernizing business processes and enhancing operational efficiency through innovative technology solutions.

5 thoughts on “What is Microsoft Power Platform? A Comprehensive Guide 2024”